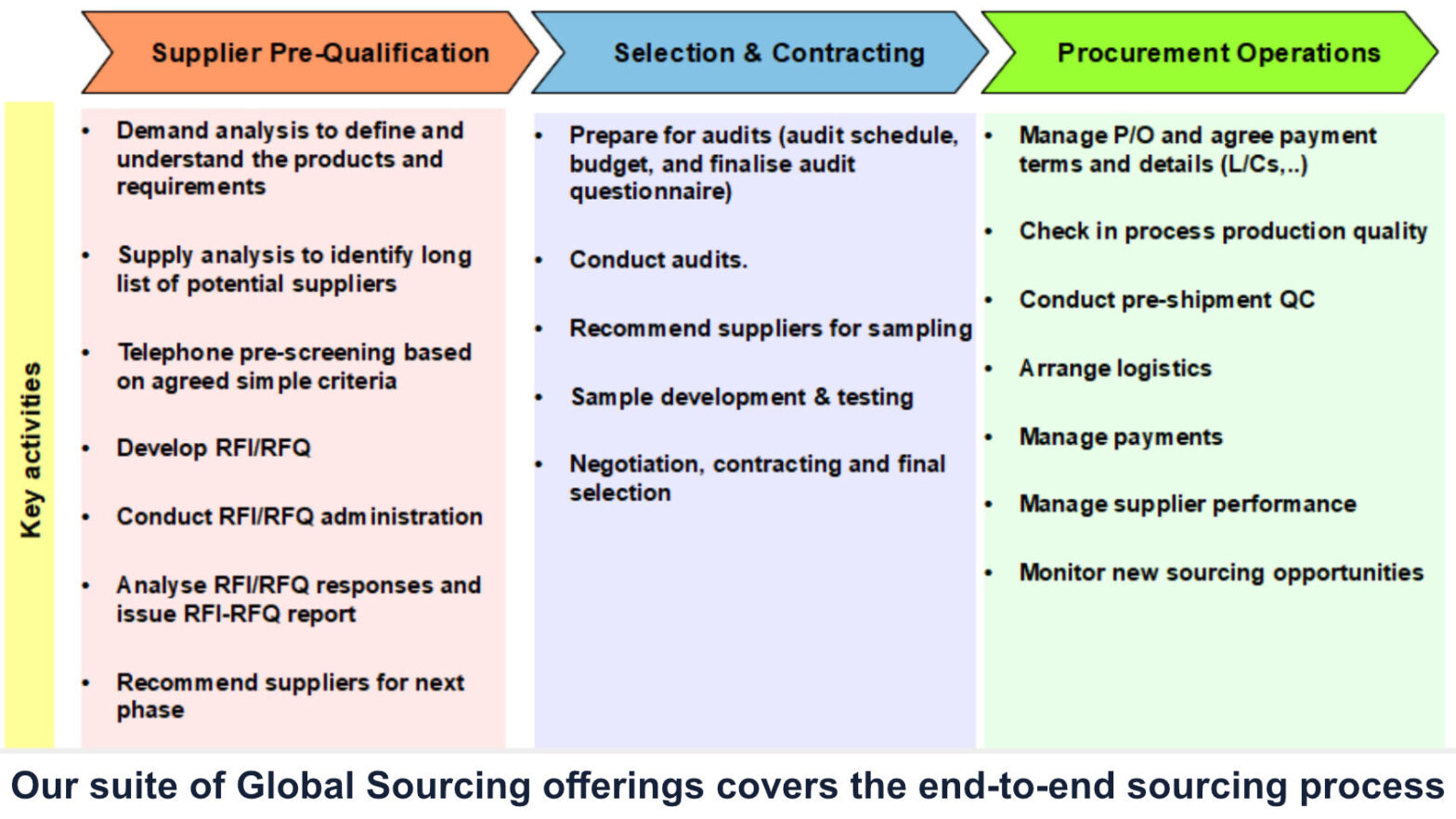
Rigorous Strategic Sourcing Foundation
Dragon Sourcing’s methodology aims to rapidly demonstrate savings to the bottom line whilst being highly analytical to make objective supplier selection decisions.
Best practices
For the Benefit of the Buying Organisation
Our business model is to work exclusively for the benefit of the buyer with no preferred relationship with any of the suppliers. In this way we are totally focused towards achieving our clients objectives and continuously improving their procurement performance.
Total Transparency & Auditability
We share all supplier information with clients with total transparency to build strong relationships built on trust and reliability. All supplier interactions are documented and are available to be audited.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to the most frequently asked questions. Please feel free to contact us. Use our contact form to describe the support you are looking for.
We can source any product or service from commodities to custom developed products. Check our Category Expertise section to see the range.
We work with small, medium size and multi-national companies that are looking to procure goods and services from emerging markets for export or to support their local operations.
We are supplier independent, we never take commissions from suppliers, and we conduct our procurement on an objective and documented basis.
From initial brief to quantifying the potential value opportunity, takes between a few days for categories we know well to 2 months for new categories.
To qualify a new supplier that has been identified as offering potential value, takes between a few weeks for simple off-the-shelf products to several months for complex custom engineered products.
contact us to discuss your requirements.


