Executive Summary: A Research Paper
Global sourcing is entering a fresh new era where companies have to use advanced technologies (especially AI), sustainability mandates, and a renewed focus on regional diversification (meaning nearshoring) are reshaping buyer strategies. Procurement teams of the organizations are adopting generative AI rapidly, companies are embedding ESG into supplier selection, and buyers are transforming supplier footprints to lower geopolitical and logistics risk. This report researches recent evidence and market signals to provide realistic guidance for procurement leaders planning 2026 sourcing strategies.
Key takeaways
- Procurement teams understand that a significant transformation is happening, so they are actively utilizing generative AI in their workflows.
- In procurement, sustainability plays a major role in mainstreaming, but measurable supplier-level targets remain less pervasive — creating audit and consultancy demand.
- In this field, nearshoring continues to grow as a strategic demand to trade friction and logistics uncertainty; Mexico, India, Vietnam, and parts of Eastern Europe are primarily in an advantageous position.
- Supplier risk is in multi-dimensional (geopolitical, climate, regulatory, and concentration) areas and requires integrated data, modeling, and local partner networks.
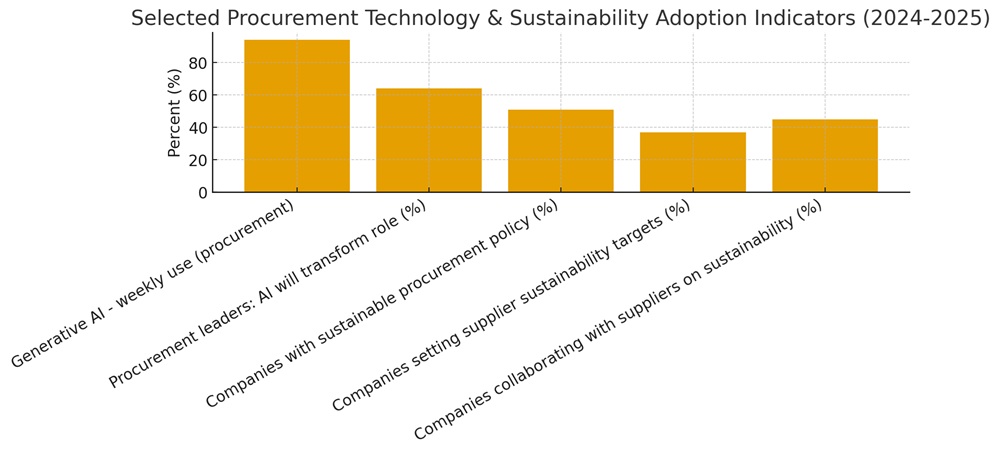
Table A — Key Research Sources and Notes
| Source | Date / Publisher | Key Insight | Reference / Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Art of Procurement – State of AI in Procurement | May 2025 | 94% of procurement professionals use generative AI weekly; highlights AI-driven sourcing transformation. | Reports AI integration accelerating strategic sourcing. |
| The Hackett Group – 2025 Procurement Outlook | April 2025 | 64% of procurement leaders believe AI will transform their roles by 2026. | Shows leadership focus on AI adoption and efficiency. |
| Procurement Tactics / Stanford Business Summary | 2025 | 51% of companies have sustainable procurement policies. | Indicates mid-level maturity in sustainability governance. |
| JAGGAER – Sustainable Procurement Report | September 2024 | 37% of firms set supplier sustainability targets; 45% collaborate directly with suppliers. | Highlights lag in supplier engagement on ESG targets. |
| Deloitte – Nearshoring and Manufacturing in Mexico | 2023 | Nearshoring trend gaining momentum for cost and resilience benefits. | Illustrates relocation strategy for supply stability. |
| IBEF – India Manufacturing & Export Trends | 2024–2025 | India sees 12% YoY growth in manufacturing exports. | Contextualizes India as a key sourcing hub. |
| WTW – Global Supply Chain Risk Report | 2025 | Discusses data-driven risk modeling in procurement. | Reinforces need for predictive risk management tools. |
| WEF – Global Risks Report | 2025 | Supply chain disruptions remain a top 5 global risk. | Underlines urgency for resilient sourcing strategies. |
| Proxima – Global Sourcing Risk Index | 2025 | Benchmarks sourcing risk across 40+ economies. | Offers comparative insights for procurement decision-making. |
Why 2026 is a turning point
The 2020s faced a number of shocks – pandemic devastation, tensions in trade, shortages in components, and climate events—that exposed the limits of highly concentrated supplier networks. Business houses that previously worked purely for unit cost are changing to multi-criteria sourcing, where resilience, transparency, and ESG performance carry a big weight. The World Economic Forum and major risk consultancies mention that updated technology and geopolitical fragmentation remain top risks for global trade planning.
AI in procurement: from automation to decision intelligence
Recent surveys mention the gigantic workflow of generative AI and other AI tools within procurement functions. One industry aggregate report shows use of generative AI among procurement professionals is very high on a weekly basis, while other analyst research finds that many procurement leaders expect AI to materially transform their roles. This quick adoption is enhanced by practical applications that include automated RFx drafting, supplier discovery, spend categorization, anomaly detection, and predictive scoring of the performance of the suppliers.
Practical impact (what buyers see now)
- Supplier shortlists on a quick basis (reduced time-to-source).
- Leveraged spend clarity from computerized classification and exception detection.
- Early-warning signals for supplier distress are good when AI ingests payment, logistics, and news data.
Implementation notes
- AI is good as per the data pipeline: poor supplier master data, missing contract metadata, or inconsistent spend taxonomies lower the value.
- Procurement teams benefit most when AI helps — not replaces — an experienced category manager.
(See Figure: comparative adoption/engagement indicators for procurement technology & sustainability.)
Sustainability: policy momentum, execution gaps, and ROI
Sustainability in procurement is now mandatory. Organizations now have sustainable procurement workflows; however, fewer of them have robust supplier-level targets and ongoing agreement programs to enhance supplier sustainability. This difference—policy vs. executed supplier workflow—creates a demand for third-party audits, supplier upskilling programs, and tracing all the data solutions.
Measuring ROI
- Short-term ROI from working on initiatives may be shorter or sector-dependent, but medium-term benefits include reduced regulatory risk, minimized exposure to carbon-related supply disruption, and improved brand value.
- Real KPIs: supplier CO₂ footprint per unit, % of spend with certified suppliers, and supplier remediation time.
Nearshoring & regional diversification: a tactical shift, not wholesale relocation
Post-pandemic master plans in the business usually follow a “China + 1” approach rather than full replacement. Nearshoring, for example, to Mexico for U.S.-facing supply chains, and shifting non-sensitive production to India, Vietnam, or Eastern Europe are commonly used. The research shows that interest in nearshoring is strong, but it works gradually and is influenced by infrastructure, skills, and incentive programs.
How to prioritize regions (quick checklist)
- Match supplier capability to product complexity (simple assembly vs. high-precision electronics).
- Evaluate total landed cost (labor + transport + tariffs + inventory-to-market).
- Assess local ecosystem (components, testing, and R&D capability).
- Factor political and trade risk (tariff scenarios, bilateral tensions).
Supplier risk: multi-factor scoring and the value of local intelligence
The supplier faces many issues, like political/regulatory exposure, climate change, financial health, concentration risk, and ESG non-compliance. Proprietary risk shows that combining those signals provides better early-warning utility than single-dimension checks. The buyers need to combine quantitative scoring with on-the-ground due diligence and periodic audits—Dragon Sourcing can provide the strategic sourcing services.
Suggested supplier risk playbook
- Need to build a tiered supplier inventory with a criticality scoring facility.
- Update a composite risk index (political, climate, financial, concentration, ESG).
- Develop the audits and remediation plans for top-risk suppliers.
- Create alternate supplier resources for critical categories.
Regional outlook (short)
- Asia-Pacific: Many Asia-Pacific countries have the manufacturing backbone for electronics and textiles. Like India, it is rapidly expanding electronics and higher-value manufacturing supported by incentives and OEM interest.
- North America (incl. Mexico): Mexico offers nearshoring at lead-time and tariff advantages for U.S. buyers; outsourcing is industry- and product-specific.
- Europe: Here the major things are ESG and automation; nearshoring to Eastern Europe for EU markets remains attractive.
- Africa: Developing opportunity; needs investment in supplier development and logistics to be competitive at scale.
Recommended actions for procurement leaders (2026 playbook)
- Adopt AI in prioritized pilots — Spend time with analytics and supplier discovery pilots; measure time and cost savings.
- Convert sustainability policy into supplier programs — Create supplier-level KPIs and finance supplier remediation where needed.
- Design a hybrid footprint — Develop “China + 1 + nearshore” depending on category risk and margins.
- Invest in supplier risk intelligence — Together indices, on-the-ground audits, and insurance/contingency plans.
- Partner with local sourcing experts — For faster work, compliance checks, and supplier development (this is where Dragon Sourcing’s network adds speed and coverage).
Primary sources used
- Art of Procurement — State of AI in Procurement (May 2025).
- The Hackett Group — procurement AI adoption analysis (Apr 2025).
- JAGGAER / CIPS sustainability procurement briefs (2024–2025).
- Deloitte & other nearshoring analyses; India manufacturing reports (IBEF, Reuters coverage).
- Global risk & sourcing indexes (Proxima, WTW, WEF Global Risks Report 2025).


